HbA1c is a marker used to measure long-term blood sugar (glucose) levels.
Those with type 1 or type 2 diabetes may have seen it before, but what is a normal HbA1c range?
This article explores what your HbA1c reading should be and how you can improve it.
What is HbA1c (Hemoglobin A1c)?
HbA1c is a marker that can determine your average blood sugar (glucose) levels over the previous 3-months (1).
That means it can be used to assess the quality of your diabetes management, as well as to diagnose pre-diabetes and diabetes.
Sometimes HbA1c is also called glycated hemoglobin, hemoglobin A1c or just A1c.
The ‘Hb’ refers to hemoglobin, a part of red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout your body.
‘A1c’ refers to a minor part of hemoglobin that sugar molecules attach to.
The amount of sugar attached is directly proportional to the amount of sugar in your blood at a given time, so this reading is used to accurately reflect average blood sugar levels.
If you’ve had high blood sugar levels in the past month or so, your HbA1c levels will be higher too.
Summary: HbA1c is a marker that reflects your average blood sugar levels in the previous 3 months. It’s also called glycated hemoglobin, hemoglobin A1c or just A1c.
Normal HbA1c Range
The HbA1c test is measured as either a percentage or in mmol/mol.
Below I’ve listed what is considered a normal HbA1c range, and what values would be considered outside of normal (pre-diabetic or diabetic):
HbA1c range for normal (non-diabetic) adults:
- Below 6.0%, or below 42 mmol/mol
HbA1c range for pre-diabetes:
- 6.0% to 6.4%, or 42 to 47 mmol/mol
HbA1c range for diabetes:
- 6.5% or above, or 48 mmol/mol or above.
Target ranges are also shown below in this table:
HbA1c | % | mmol/mol |
| Normal | Below 6.0% | Below 42 mmol/mol |
| Pre-diabetes | 6.0% to 6.4% | 42 to 47 mmol/mol |
| Diabetes | 6.5% or above | 48 mmol/mol or above |
Normal HbA1c Range For Diabetes
Those with diabetes are advised to aim for a HbA1c level of:
- 6.5% or 48 mmol/mol.
A value lower than this 6.5% target indicates great blood sugar control, a value higher indicates the need for improvement.
Now this range is 0.5% higher than the normal range given for those without diabetes, as it’s unlikely that diabetes patients can match that exact same blood sugar control.
In fact, some experts believe a more realistic healthy range for diabetics should be 7-7.5%.
Summary: The normal HbA1c range is below 6.0% for the average adult, and 6.5% or less for those with diabetes. Some argue the the normal range should be slightly higher for diabetics.
Testing HbA1c Levels vs Blood Glucose Finger Prick
The typical fasting blood glucose finger prick shows your blood sugar levels right at that moment.
These are (confusingly) measured in mmol/L or mg/dL.
Measuring HbA1c levels instantly provides a bigger picture view, kind of like an average of your blood sugar levels over the past 3 months.
It’s usually taken from your regular arm blood test rather than the finger prick.
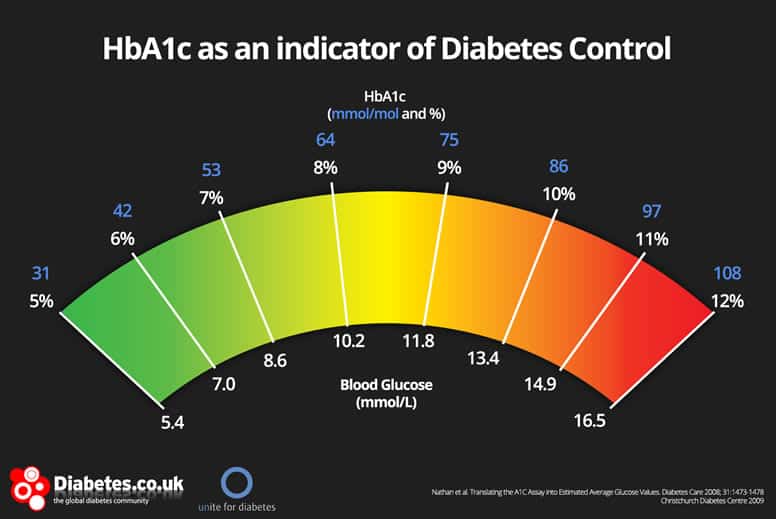
This HbA1c chart shows how the different tests correlate with one another. HbA1c levels are shown at the top, and blood glucose (the finger prick test) is shown below:
Click to enlarge. Image source
As an example, if your average blood glucose (sugar) reading in the finger prick tests is around 10.0 mmol/L, then your HbA1c level will be about 8%.
Said another way, if you get a HbA1c of 9% then we know your average blood glucose level is about 11.8 mmol/L for the past few months.
Here’s another HbA1c chart that shows those comparisons side-by-side:
| HbA1c levels (%) | HbA1c levels (mmol/mol) | Blood Glucose (mmol/L) |
13 | 119 | 18 |
12 | 108 | 17 |
11 | 97 | 15 |
10 | 86 | 13 |
9 | 75 | 12 |
8 | 64 | 10 |
7 | 53 | 8 |
| 6 | 42 | 7 |
Summary: The blood glucose finger prick shows your current blood sugar levels, whereas HbA1c is representative of your previous 3-month average.
Risks of a High HbA1c Levels
HbA1c is an important marker because it can estimate the health risks associated with high blood sugar levels.
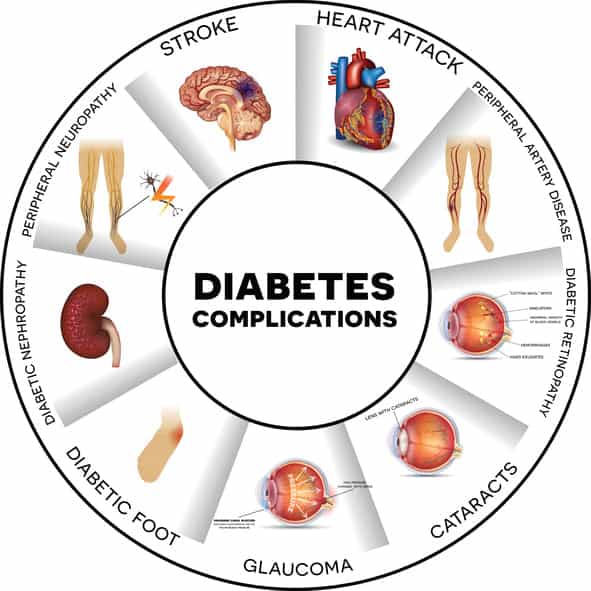
Studies show those who can lower their HbA1c by just 1% (11 mmol/mol) will (2, 3):
- reduce their risk of neuropathy (damage to nerve endings) by 25%
- reduce their risk of retinopathy (damage to eye retina) by 25%
- reduce their risk of diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease) by 25%
- reduce their risk of heart failure by 15% for every 1% drop in HbA1c
- reduce their risk amputations and vascular disease by 43%
- reduce their risk of cataracts by 19%.
These numbers are based on observational data and therefore would vary somewhat between people. But they paint a powerful picture.
For example, reducing your HbA1c from 9% to 7% will cut your risk of neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy by half and almost all chance of vascular disease. Risk of heart failure and cataracts is also slashed by up to 38%.
Summary: HbA1c is a strong predictor of various major health issues related to diabetes.
Improving HbA1c and Diabetes Management
If you’re showing signs of high blood sugars or have a high HbA1c level then there are many things you can try (other than medications like metformin).
Regular exercise is very important, as is maintaining a healthy weight.
But I’d argue that diet changes should be your first priority. Consider:
-
reducing your carbohydrate intake (after speaking with your doctor)
-
choosing lower-sugar snacks
-
and even eating more of these diabetes-friendly foods.